We’ve already introduced terpenes as a whole. That said, in this article, we’ll focus on just one: linalool. In the rest of this article, we’ll see what it is in detail. So, let’s get down to business! Linalool in BriefIndeed, as always, let’s start by presenting our terpene in general terms. Then, we can emphasize some more specific and technical considerations. So, what points can we focus on? We suggest the following: the element itself, its characteristics, the plants that contain it, and its role.
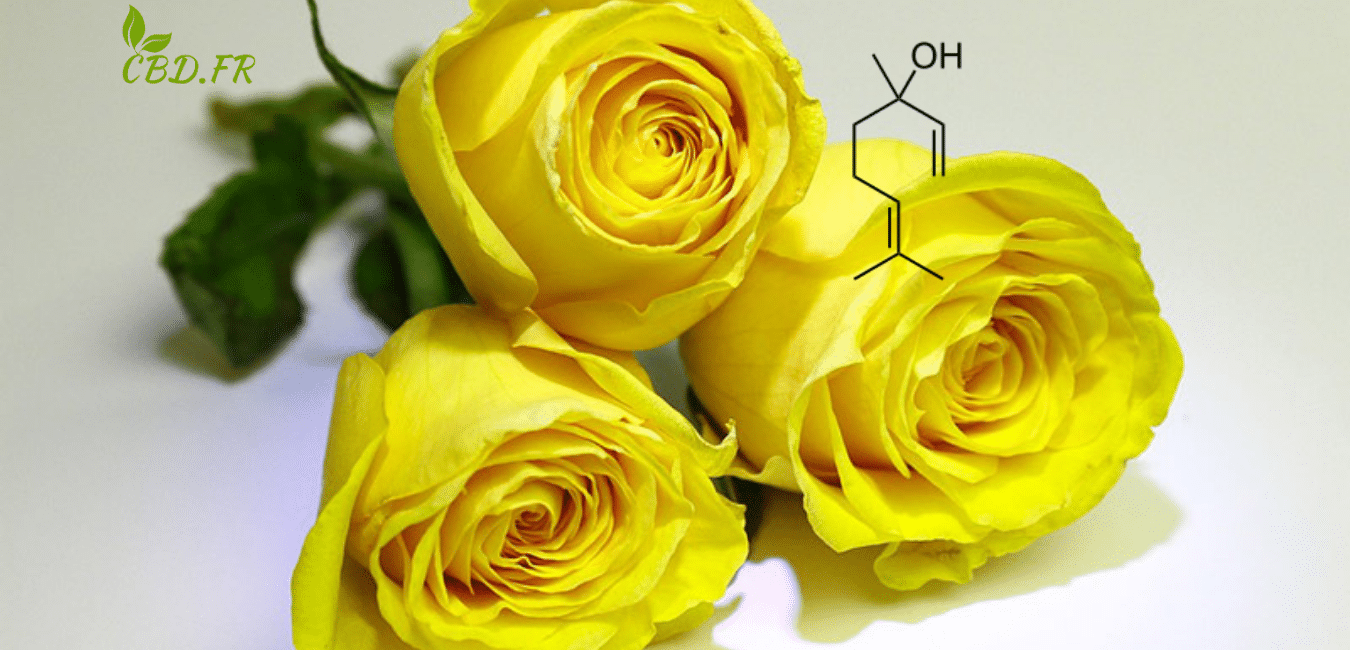
First, let’s introduce linalool and indicate the main plants in which it is found. To that end, we refer to this Wikipedia article. It clearly explains all these details. So, let’s read carefully! Linalool (3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-ol) is a terpene alcohol, an unsaturated tertiary alcohol with a fresh, floral scent. It is found in a majority of essential oils, notably lavender, bergamot, rosewood (where it is the major component), and mint. This organic compound is slightly soluble in water.
Source: https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linalol In fact, we can glean quite a bit of information from the previous quote. First, other names for our terpene include: linalool, 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-ol. Second, it is present in various essential oils. Finally, it offers a fresh, floral scent. This last detail allows us to highlight the unique characteristics of this terpene. On the other hand, let’s talk about what’s special about linalool.
As mentioned above, linalool’s aroma makes it unique. It offers a scent that’s difficult to define: floral, fresh, tangy, and slightly spicy. It’s precisely this aromatic complexity that makes it even more appealing. Furthermore, what about the plants that contain it? There are many, but the hemp/cannabis plant is a prime example. Others include silver mint, spearmint, birch bark, rose, lavender, basil, grape, and lemon. Of course, this list is incomplete! We’ve only included a few examples to illustrate the point. From this perspective, what is its role within these plants? On the one hand, it gives them its unique scent. This is obvious, as we discussed earlier. On the other hand, it acts as a secondary metabolite in these species. In other words, linalool indirectly contributes to the growth and development of the organism. Its strong odor helps repel herbivorous predators and harmful insects.
Chemical and Physical Properties of Linalool
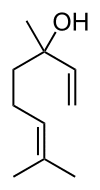
Indeed, we are dealing with a compound that can be studied in the laboratory. Therefore, it would be worthwhile to examine its physicochemical properties. So, let’s begin! Structure
It is as follows. LinaloolCredit: Wikipedia
Identification
The data used to identify it are as follows. IUPAC Name:
Sommaire
Toggle3,7-Dimethylocta-1,6-dien-3-ol
Synonyms: linalyl alcohol, linalool
CAS No.: 78-70-6
ECHA No.: 100.001.032
PubChem No.: 6549
ChEBI No.: 17580
- FEMA No.: 2635 Appearance: Colorless liquid with a characteristic odor.
- Chemical Properties:
- These are as follows. Chemical formula: C10H18OMolar mass: 154.2493 ± 0.0096 g/mol C 77.87%, H 11.76%, O 10.37%
- Physical propertiesThese are presented below. Melting point: -28.25 °C
- Boiling point: 198 to 200 °CSolubility: in water at 25 °C: 1.6 g/L Density: 0.9 g/cm³
- Auto-ignition temperature: 235 °CFlash point: 75 °C Explosive limits in air: 2.97% vol
- Saturated vapor pressure: at 25 °C: 21 Pa
- Uses of linalool
- In fact, this terpene joins many others that exist. To what extent? In that it, too, is used in various sectors of activity. That said, we will only address two.
Firstly, the cosmetics industry. Indeed, above, in its brief introduction, we touched on this aspect. Linalool is mainly used in the manufacture of essential oils. These are becoming increasingly popular worldwide.
- Furthermore, this terpene plays a significant role in the pharmaceutical industry. How can this be explained? In fact, it is believed to be responsible for a number of effects beneficial to drug manufacturing. The following are some examples.Anticonvulsant (for more details, see the anticonvulsant benefits* in humans)Sedative (This 2009 article** discusses this)Anxiolytic (This research*** published in the journal
- The Mental Health Clinician discusses this. You can also consult this other research**** published in The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology
. The same applies to this study*****)
Analgesic (This study****** published in the
- European Journal of Pharmacology
- sheds light on this)
- Antidepressant (This research******* published in 2013 mentions this. You can also add this article******** published inLife Science
- )Finally, it should be noted that this terpene,
- linalool
- , is naturally present in
- CBD flowers
- .
Also read.
Nerolidol Terpinolene Limonene
Terpenes
- Humels
- References:
- *ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28826544 **ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18824339 ***ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6007527/ ****ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25522403/*****sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0944711309002578
- ******sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S001429990202856X*******link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11418-013-0751-6 ********sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0024320515001381