In a previous article, we explored THC Delta 10. That said, let’s continue this overview of the different isomers of the THC molecule. For those who haven’t read the aforementioned article, an isomer refers to a compound with the same overall formula as another, but different properties due to a different arrangement of atoms within the molecule. The two cases we’re interested in here are: THC Delta 8 and THC Delta 9, two forms of tetrahydrocannabinol. The goal of this article is to understand the difference, distinguish between them, and learn more about CBD.
Sommaire
ToggleMeaning of THC
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is a substance found in cannabis that is of great interest, particularly because of its psychoactive effects. In this article, we shed light on the concept of normal THC levels, the definition of THC, and its significance for consumers and professionals.
Definition of THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
THC is one of the many cannabinoids found in cannabis plants, such as marijuana and hemp. It was first identified in 1964 by Israeli scientists Raphael Mechoulam and Yechiel Gaoni. Since then, it has become the most studied and well-known cannabinoid among the general public. THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, meaning it causes changes in perception, behavior, and consciousness. CB1 receptors in our central nervous system interact with THC, triggering these sensations as well as the release of dopamine, which is responsible for the feeling of euphoria and well-being often associated with cannabis use. THC and Other Cannabinoids
In addition to THC, cannabis plants also contain other important compounds called cannabinoids.
such as CBD (cannabidiol). CBD is another cannabinoid that also has medicinal properties, but unlike THC, it does not produce psychoactive effects and is therefore not responsible for the “high” felt when consuming cannabis.
What is a normal THC level?
There is no universal answer to this question, as the notion of a “normal THC level” can vary depending on several factors, such as:
The strain of the cannabis plant
- The cultivation method
- The preparation or processing method for derivative products
- Local and national laws regarding the possession and use of cannabis products
- Cannabis plant strain: influence on THC level
Some cannabis strains are naturally richer in THC than others. Generally, we distinguish between:
Indica strains:
- These generally have a lower THC level than sativa strains and are often used for their relaxing and calming effects. Sativa strains: These produce an energizing and stimulating effect, thanks to a higher concentration of THC.
- Hybrid strains: Resulting from the crossbreeding of indica and sativa, their cannabinoid profile can vary considerably, including THC concentration. Legislation and Normal THC Levels The legality of cannabis and cannabis-derived products varies from country to country. Some countries allow the medical or recreational use of cannabis with specific THC concentrations. For example:
- In the United States, some states allow marijuana for adult use by individuals over 21 years of age, while others only allow medical use with a prescription. THC concentration thresholds also vary depending on the different state laws. In the European Union, cannabinoids are subject to strict regulations that generally prohibit the sale and consumption of cannabis products containing more than 0.2% THC.
The Effects of THC Levels in Cannabis
- The
- potency
of a cannabis product is directly related to its
THC concentration. In fact, the higher the THC content, the more intense and rapid the psychoactive effects will be. However, it should be noted that each person is unique and there is significant individual variability in sensitivity to THC. Thus, the same dose of THC can produce very different effects from one person to another, depending on factors such as:Individual metabolism
Consumption habits and tolerance to THC
- Genetic susceptibility to psychoactive effects
- It is also important to consider other cannabinoids present in cannabis, such as
- CBD.
Studies have shown that the presence of CBD can mitigate or counteract some of the effects of THC, thus reducing its overall potency. THC Levels in Different Forms of CannabisCurrently, consumers can find a variety of products containing THC, each with varying concentration levels:
Cannabis Flowers:
These represent the traditional form of the plant, and the THC concentration can vary between 1% and 35% depending on the strain, cultivation methods, and how they are dried and stored.
- Oils and Tinctures: These offer a more concentrated formulation by directly extracting the cannabinoids from the plant in liquid form. Tinctures typically contain between 40% and 80% THC.
- Concentrates and Extracts: These include products such as resins and waxes that have undergone a specific extraction process to obtain a highly concentrated THC product, with concentrations reaching up to 90%.
- Edibles: They are increasingly popular, and the THC content can vary considerably from one product to another, from a few milligrams to several hundred milligrams of THC per serving.
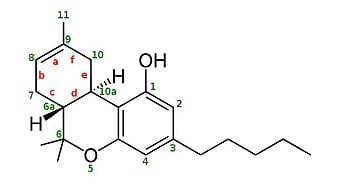
- What are Delta 8 THC and Delta 9 THC? On the one hand, Delta 8 THC is an isomer (a form) of THC. Also known by the following names: Δ8-THC, Δ-8-THC, Δ8-THC, δ-8-THC, Delta-8-THC, Delta-8-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Δ-8-tetrahydrocannabinol. This variant occurs naturally in both the hemp plant and the cannabis (or marijuana) plant. It is important to note that its concentration is low. In other words, it is present in small quantities in these plants. Its structure is as follows. THC Delta 8
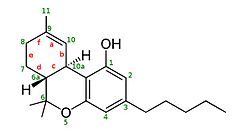
On the other hand, and in parallel, THC Delta 9 is also known as
Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinolIn fact, at the beginning of this article, we included Delta 9 in the category of THC isomers. However, this isn’t entirely accurate. Why? Because it is actually the THC molecule itself. The name used at the beginning of this article is simply less well-known. That being said, this component is naturally present in the aforementioned plants. Specifically, it is found in large quantities in cannabis (or marijuana). Its structure is as follows: Delta-9-THCBoth have a maximum legal limit of 0.2% in the European Union. What are the effects of THC Delta 8 and THC Delta 9? These two components have numerous effects. We present the most important ones below.
On the one hand, in some people, Delta 9 THC can induce feelings of anxiety. Similarly, it could also cause paranoia for no apparent reason. This study also states that it could have an effect on mental performance. On the other hand, the THC Delta 8is said to be less psychoactive than Delta 9. Many argue that it is less potent.
On the one hand, being very potent, Delta 9 THC is more likely to induce euphoria than relaxation. Many people report a feeling of “high,” sometimes even euphoria, after taking THC. On the other hand, Delta 8 leads to relaxation, without the “high.”
Speed of absorption
Delta 9 is said to be absorbed quickly by the user’s body. This, in turn, means that the effects are felt much faster. Delta 8, on the other hand, takes longer to absorb. Therefore, the effects are gradual and mild.
- Why is there no THC in CBD? Cannabidiol, more commonly known as CBD, is a chemical compound found in the cannabis plant. Contrary to popular belief, this compound is not psychoactive and therefore does not produce psychotropic effects, unlike tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), another well-known compound in the cannabis plant. But why is there no THC in CBD? To answer this question, several aspects must be considered. The Difference Between CBD and THC Before understanding why CBD contains little to no THC, it is important to know the main differences between these two compounds. The molecular structure of the two cannabinoids is extremely similar: they both share 30 hydrogen atoms (H), 21 carbon atoms (C), and 4 oxygen atoms (O). However, it is the arrangement of these atoms that makes all the difference. Effects on the Body
- THCTHC is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, such as euphoria, drowsiness, and increased appetite. These effects are due to its interaction with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), specifically with the CB1 receptor located primarily in the brain.
- In contrast, CBD acts differently on the body and is not psychoactive. It can even moderate the effects of THC when consumed together. CBD interacts with the ECS’s CB2 receptors, which are primarily located in the immune system and peripheral organs. Its action on these receptors allows it to have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic effects, without causing addiction or impairing cognitive function.
Separating CBD and THC during extraction: Even though the cannabis plant contains both CBD and THC, it is possible to extract only the CBD while avoiding any THC contamination. Several extraction methods exist for this purpose:
Supercritical CO2 extraction: This technique uses carbon dioxide under high pressure to extract chemical compounds (including CBD) from the cannabis plant. It allows for excellent separation between CBD and THC and guarantees a very pure final product. Solvent extraction: The cannabis plant is soaked in a solvent (such as ethanol) which dissolves the cannabinoids. After the solvent evaporates, a more concentrated CBD extract, free of THC, is obtained.Selective filtration extraction: This method involves filtering the plant material suspended in a liquid through specific membranes, which retain the THC molecules while allowing the CBD to pass through.
Techniques to guarantee a THC-free product
Beyond the extraction methods listed above, certain precautions can be taken to ensure the final product contains as little THC as possible:
Use cannabis plants with a low THC content: Some cannabis varieties are naturally richer in CBD than THC. Choosing these varieties for extraction allows you to obtain products that are almost THC-free from the start.
Conduct laboratory tests: Reputable manufacturers of CBD products voluntarily undergo regular and rigorous quality controls to verify the THC content and guarantee a safe product that complies with the law. Is Delta 8 legal in France? The legality of Delta 8 in France can be confusing due to constantly evolving laws and regulations. In France, the list of narcotic substances includes “Tetrahydrocannabinols,” which includes Delta 8, making its possession and consumption illegal. However, it’s worth noting that the origin of Delta 8, whether it comes from hemp or CBD, does not affect its legal status in France.
In short,
in France, Delta 8 is currently considered illegal.
- This is a reality that could change over time with regulatory changes worldwide.
- What is the threshold for testing positive for THC?
- Testing positive for THC, the main psychoactive component of cannabis, depends on several factors. For occasional use
Traces of THC can be detected in urine for 3 to 5 days and in blood for 2 to 8 hours. For regular use, these durations extend to 30-70 days and several weeks respectively after the last use.
It should be noted that the level of THC-COOH (a THC metabolite) can remain detectable in the blood for up to 72 hours.
- The type of test used must also be taken into account. For example, a saliva test detects THC for 6 to 8 hours after occasional use, with a detection threshold of 15 ng/ml. Finally, a hair follicle test establishes a positive result at 0.1 ng/mg for THC, with the detection time depending on hair length.
- What molecule destroys THC? The breakdown of THC in the human body is a complex process that primarily involves the liver. Indeed, it is the cytochrome P450 enzyme, present in the liver, that plays a major role in the metabolism of THC.
The THC molecule is transformed into several metabolites, the main one being 11-hydroxy-THC, which is itself converted into THC-COOH (11-nor-9-carboxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol), a non-psychoactive compound. This is then eliminated from the body through urine and feces.
It should be noted that the time required to metabolize THC varies depending on several factors, such as individual metabolism, frequency of consumption, and the amount of THC consumed.